OUR TESTING APPLICATIONS
Acoustic testing methods are becoming increasingly important for quality assurance in serial production. Acoustic testing is a comparative testing technology which means that a feasibility study based on reference components (accepted/rejected) must always be performed prior to configuring a testing system. Depending on the acoustic testing application and requirements, we use the appropriate acoustic emission sensors, microphones and/or laser vibro-meters to acquire sound and vibrations.

Acoustic material testing
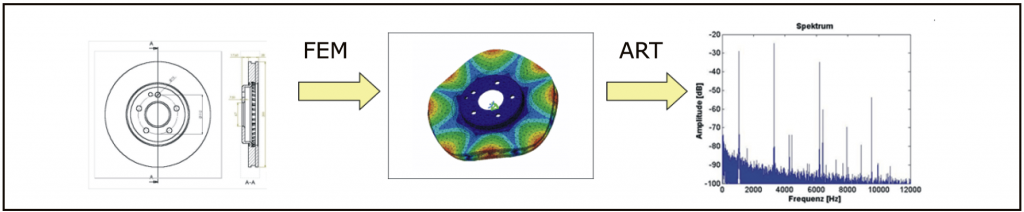
Acoustic resonance analysis, also known as sound testing, is a non-destructive testing method (NDT) that enables fast and cost-effective testing of a large range of workpieces. It exploits the physical phenomenon of a body vibrating in response to an appropriate stimulus (e.g. impact), with specific characteristic natural modes and frequencies. This is the “language” of the workpiece. These sounds are used to assess the dynamic strength of the component, because any cracks, defects or other abnormalities in the material structure cause a change in the resonance spectrum. Acoustic material testing is a comparative test, where serial parts are tested against the resonance spectrum of so-called master parts (good and reject parts).
Acoustic resonance analysis is a volume testing method that evaluates the workpiece as a whole. In contrast to surface-specific methods such as endoscopy, dye penetrant inspection or magnetic particle testing, it enables a particularly fast and cost-effective evaluation of changes in the component’s bulk structure.
Testing technology
With SonicTC.AT, RTE offers a powerful system with a comprehensive selection of evaluation algorithms and an excellent price-performance ratio. The testing system includes a number of expansion modules, e.g. compensation procedure for unavoidable interference factors during the production process (batch, ageing, temperature). Results can be documented quickly and easily. Additional information about SonicTC.AT.
Benefits
Customers will be impressed with the quality of your deliveries!
- This method can detect defects which other NDT methods cannot detect, or only detect in some cases
- You save on consumables and waste disposal costs
- Acoustic methods are environmentally friendly
- No chemical or radioactive additives are needed
- Quality decisions are made impartially and reliably, instead of subjectively and with uncertainty
- Acoustic methods are easy to use and safe
- Personnel do not need to be certified
Applications
- Material testing, crack testing, structural testing, identification testing
- Resonance analysis, sound analysis, sound evaluation, sound sampling, sound testing
- Structural Testing, Ductility, Nodularity
- Natural frequency analysis, natural frequency measurement, natural frequency testing
- Cast metals, magnetic and non-magnetic metals, ceramics, sintered products, glass
- Alternatives or replacements for dye penetrant testing, eddy current testing, ultrasound, magnetic particle testing, X-ray testing
Research


Natural frequency and Q-Factor measurement
The natural frequency of a vibrating system is the frequency at which it oscillates following a single excitation.
For measurements of natural frequency, the way in which the object to be measured is mounted (so that it can vibrate), the point of impact, the choice of sensors and, if applicable, also the degree of ageing and temperature of the object to be tested, must be taken into account.
Testing technology
With SonicTC.Natural Frequency, RTE offers a powerful system with short cycle times and an excellent price-performance ratio. The testing system includes a number of expansion modules, e.g. compensation procedure for unavoidable interference factors during the production process (batch, ageing, temperature). Results can be documented quickly and easily.
Benefits
- Excellent price-performance ratio
- Suitable for different products with minimal retrofitting costs
- Guaranteed compliance with customer and DIN requirements
- Modular extensibility ensures long-term viability
- Reliable natural frequency data as a result of multi-position measurements and age compensation
- The extra edge: Damping and quality evaluation
Applications
The measurement and monitoring of natural frequencies ensures that a component or assembly will not generate unwanted vibrations once installed in a system.
Requirements for components of brake systems such as brake discs, apply to all vehicle and vehicle component manufacturers and are defined in the European Brake Noise Expert Group’s EKB 2002 serial test specification.
Research


Noise and vibration testing
One can hear whether everything is working properly or if a product is defective and a component is making unusual noise during operation. We subjectively assess quality through sound. However, objective testing is indispensable for serial monitoring and documenting supply quality. This provides you with a modern and efficient noise and functional testing system.
Miniaturised servos, steppers and motors, pumps, actuators and transmissions, extending all the way to complete assemblies can be found in practically all devices, systems, mounting systems and vehicles, and all these can be checked acoustically for quality.
Testing technology
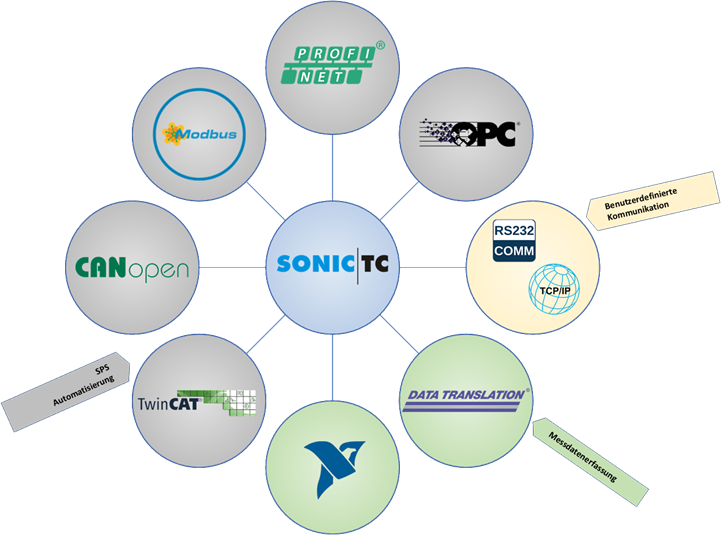
SonicTC.NVH (noise, vibration and harshness) is the new generation of acoustic testing systems for inline and end-of-line testing, with the widest range of applications. In terms of the networked “Factory 4.0”, it connects the control level (MES) to the field level.
SonicTC.NVH offers the greatest flexibility for process integration interconnectivity.
Benefits
Vibro-acoustic noise and functional testing in production can significantly improve quality assurance for products and components. Furthermore, the data can also be used for documenting and improving product and process quality. Comprehensive documentation, archiving, traceability and verification enable test results to be certified at any time. By continuously monitoring and improving production, customer complaints can be reduced to a minimum.
Applications
Example applications of our process-reliability defect detection in serial production:
- Electric actuators and motors: malfunctions and noises
- Transmissions and drives: malfunctions and noises, imbalances
- Bearings: friction and grinding noises • Gears: defective teeth, teeth meshing defects
- Drive shafts: defective surfaces and chatter marks
- Shaft imbalances or drive train imbalances
- Switching noises or relay switching

Acoustic process monitoring
Process monitoring
In many areas of production, noises and vibrations are generated during the manufacturing process. These provide information about the condition of the machine or the currently-running process. This acoustic information can be picked up by sensors and evaluated inline by the testing and measuring system. This allows actions to be triggered immediately, e.g. in the machine control system, if pre-set limits are exceeded.
The SonicTC.DSP inspection system can be applied in all sectors of industry, including the automotive and other industrial sectors. The SonicTC.DSP testing system offers reliable monitoring of production equipment such as machine tools, automatic assembly machines, presses and stamping machines for faults such as tool breakage, the presence of foreign bodies, etc.
In many cases, the monitoring function is easier to implement than anticipated by the user. For straightforward monitoring functions, RTE deploys its SonicTC.DSP solution.
Mode of operation
Workpiece machining and assembly generates noises and vibrations. When parts are being assembled, characteristic noises can be monitored to determine whether the assembly is correct or faulty. A typical final noise, such as a “click”, indicates proper execution of the assembly process.
Vibrations and noises generated as the workpiece is machined by drilling, turning, grinding, sawing or pressing allow conclusions to be drawn about the machining process and workpiece condition.